What is real?
In the age of extended reality, this question takes a new meaning. Today, technology has blurred the line between reality and digital. In this post, we want to explore the fascinating world of extended reality, and how it can help in making the real world a better place.
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Extended Reality is an umbrella term for all immersive technologies that extend reality by combining the virtual and physical worlds. The most prominent technologies are: Virtual reality (VR), Augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR)
Fun fact: X in XR doesn’t mean extended. It is used as a variable x so it can be exchanged with other letters.
Imagine virtual meetings that feel as real as in-person conversations, immersive training that saves lives, and shopping experiences where you try on clothes or test products from your living room.
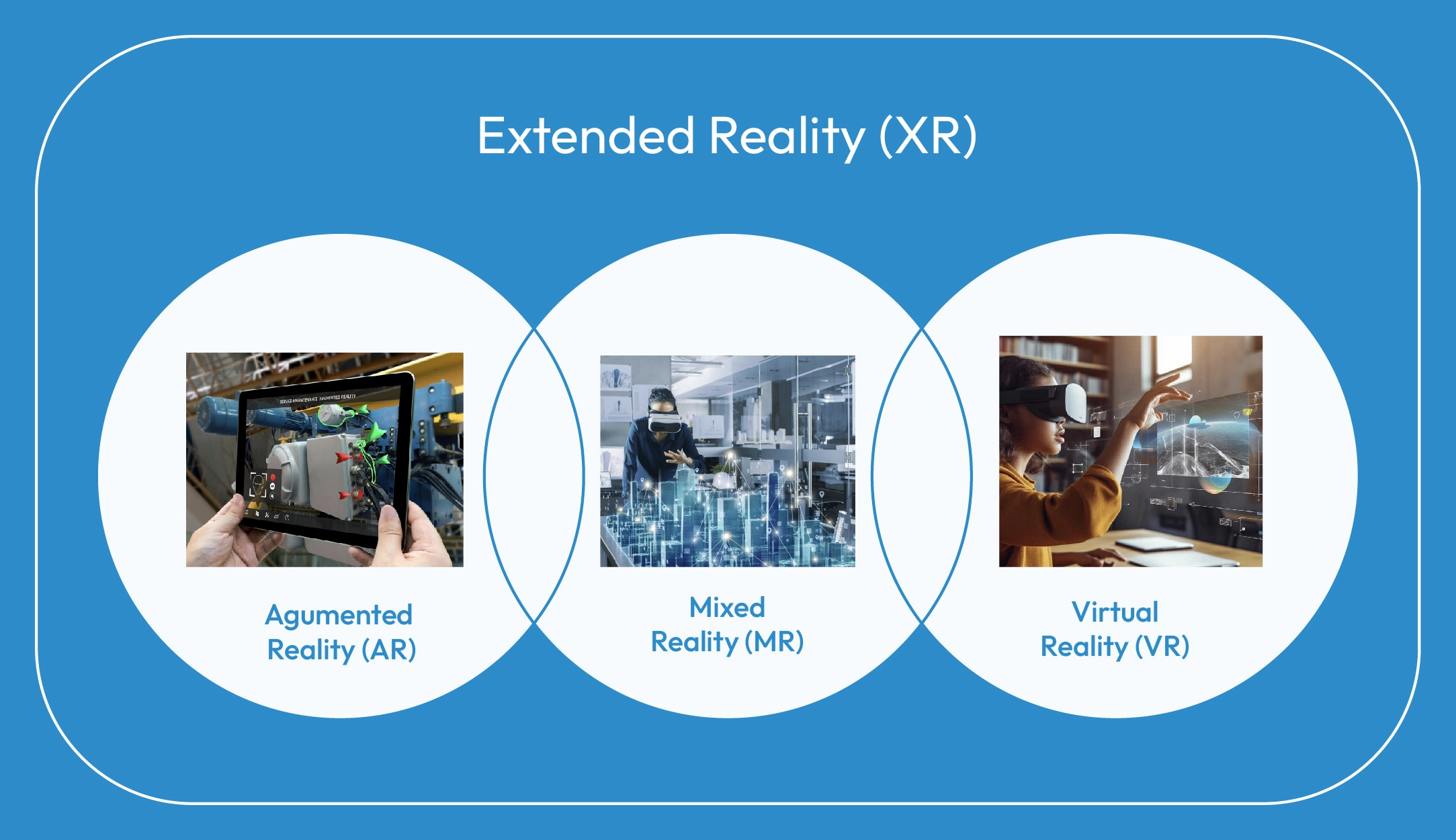
Components of Extended Reality
Virtual Reality (VR)
Fully immersive virtual /digital environments, computer generated. We need sensory simulators (for eg: head mounted display) to feel the virtual environments.
- Example devices: Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR.
- Applications: Gaming, simulations, virtual tours.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Merging of real and virtual worlds. Enhance or alter the real world rather than completely replacing it. Virtual objects are overlaid onto the real word with positional tracking.
- Example tools: ARKit, ARCore, Snapchat filters.
- Applications: Retail, Education, Marketing.
Mixed Reality (MR)
MR is any form of XR that is merging or integration of real and virtual environments.
- Example devices: Microsoft HoloLens, Apple Vision Pro.
- Applications: Design, collaboration, industrial training.
Differences between Mixed Reality and Extended Reality
As explained before, Extended Reality is a big umbrella term covering MR and other technologies.
MR is different because it allows real-time interaction between the user, the physical world, and the digital elements.
- VR: You’re completely inside the computer-made world.
- AR: The computer adds things to the real world you see (like Pokémon Go).
- MR: The computer-made things act like they’re really part of the real world (you can interact with them).
Differences between Augmented Reality and Extended Reality
On the other hand, in AR the digital content exists independently of the physical environment. The digital content is typically placed on top of the real world without much regard for how it interacts with the actual environment.
In AR, the digital content typically exists independently of the physical environment. You can place a virtual sofa in your living room, but it won’t block the light coming through the window, and you can’t sit on it.
Technologies Powering Extended Reality
Some technologies that are powering XR:
Hardware
Headsets (Oculus, HoloLens, Magic Leap) Smartphones and tablets (AR experiences) Sensors (LiDAR, cameras, haptic gloves)
Software
Development platforms: Unity, Unreal Engine, ARKit, ARCore. WebXR frameworks: A-Frame, Three.js.
Core Concepts
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) Spatial Computing Cloud Rendering
Applications of XR
Healthcare
Surgical simulations, therapy, diagnostics. Example: VR for surgery training.
Education
Immersive learning environments. Example: AR-enabled textbooks and VR field trips.
Retail and Marketing
AR try-ons and interactive advertisements. Example: IKEA Place App (AR furniture placement).
Gaming and Entertainment
VR/AR immersive gaming experiences. Example: Pokémon GO, Beat Saber.
Industrial Training
Simulations for hazardous environments. Example: AR for equipment maintenance.
Real World Examples of Extended Reality
Extended reality (XR) is no longer a futuristic concept. It’s already reshaping industries across the globe. Here are some real world examples of extended reality.
- Pokémon GO: Global phenomenon showcasing AR’s potential in gaming.
- IKEA Place App: Helping users visualize furniture placement using AR.
- VR for Therapy: Using VR to treat PTSD and phobias.
- Microsoft HoloLens in Manufacturing: Assisting workers with real-time data overlays.
Disadvantages of Extended Reality / Challenges of Extended Reality (XR)
Hardware Limitations
Expensive devices, battery life, and portability issues.
Technical Barriers
Latency, rendering quality, and field-of-view limitations.
User Experience
Motion sickness, accessibility, and user adoption.
Privacy and Security
Data collection concerns in AR/VR experiences.
What is the future of Extended Reality (XR)?
The future of XR is nothing short of revolutionary. As technology advances, XR is set to revolutionize how we live, work, and connect. Here are some exciting applications of XR in real life, that we can look forward to:
Lightweight AR Glasses -Replacing smartphones as daily devices.
Imagine if your smartphone was no longer the primary gateway to digital interactions. With advancements in AR hardware, lightweight AR glasses will replace traditional mobile devices. These smart glasses will overlay digital information onto our surroundings, enabling hands-free navigation, instant translations, real-time notifications, and even virtual assistants integrated directly into our field of vision.
Metaverse -XR as a gateway to persistent virtual worlds.
The concept of the metaverse is gaining momentum, and XR will play a pivotal role in bringing it to life. With immersive VR and AR technologies, users will be able to explore persistent virtual worlds for work, social interactions, entertainment, and education. Businesses are already experimenting with virtual offices, while online gaming and social platforms are evolving to offer richer, more interactive experiences. As XR technology matures, the metaverse will become an extension of our daily lives rather than just an online destination.
AI and XR Integration -Enhancing interactivity and content creation.
The combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and XR is unlocking new levels of interactivity and personalization. AI-driven XR applications can dynamically adjust content based on user preferences, provide intelligent virtual assistants, and create realistic digital environments that respond to real-time inputs. From AI-generated holograms for training and customer service to personalized virtual shopping experiences, this integration will redefine digital engagement across industries.
5G and Cloud XR -Enabling real-time XR streaming.
One of the biggest challenges in XR adoption has been the hardware limitations required to process high-quality, immersive experiences. However, with the rollout of 5G and advancements in cloud computing, Cloud XR is set to transform how we access XR applications. Real-time XR streaming will allow users to experience high-end AR and VR content without needing expensive, bulky devices. This will make XR more accessible to consumers and businesses alike, unlocking new use cases in remote collaboration, virtual tourism, and beyond.
Key Takeaways and Conclusion about Extended Reality
- XR is revolutionizing how we interact with digital and physical spaces.
- Applications are growing across industries like healthcare, retail, education, and entertainment.
- Challenges exist, but advancements in hardware, software, and connectivity are driving the future of XR.
- XR will play a major role in shaping the Metaverse and future immersive experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
How could the manufacturing sector utilize extended reality?
Extended Reality (XR) is transforming manufacturing by improving training, efficiency, and collaboration. AR helps in real-time guidance for workers, which reduces errors and boosts productivity. VR simulates factory layouts and processes implementations which can also identify errors and bottlenecks in time. There is scope of remote troubleshooting, predictive maintenance, etc too. These innovations will streamline operations, cut costs, and improve all safety in manufacturing.
What is the benefit of applying extended reality solutions to surgical science?
The application of extended reality (XR) in surgery enhances accuracy, training, and collaboration. Virtual reality (VR) enables surgeons to practice intricate procedures in risk-free virtual simulations. Augmented reality (AR) overlays real-time guidance during surgery, improving accuracy and lowering errors. XR enables remote collaboration, enabling professionals to assist patients from anywhere. All this enhances patient recovery and maximizes surgical processes.
.…………..
At Gurzu, we’ve explored the possibilities of XR through our work on activated products. Whether you’re looking to enhance user engagement, create immersive experiences, or bring your digital vision to life, we can help.
Let’s talk! Reach out to us to explore how XR can elevate your next project. You can also book a free consulting call with our expert.
This article is based on knowledge ketchup talk by Asmit, presented at Gurzu. You can find the original slide deck here.

